Table of Contents
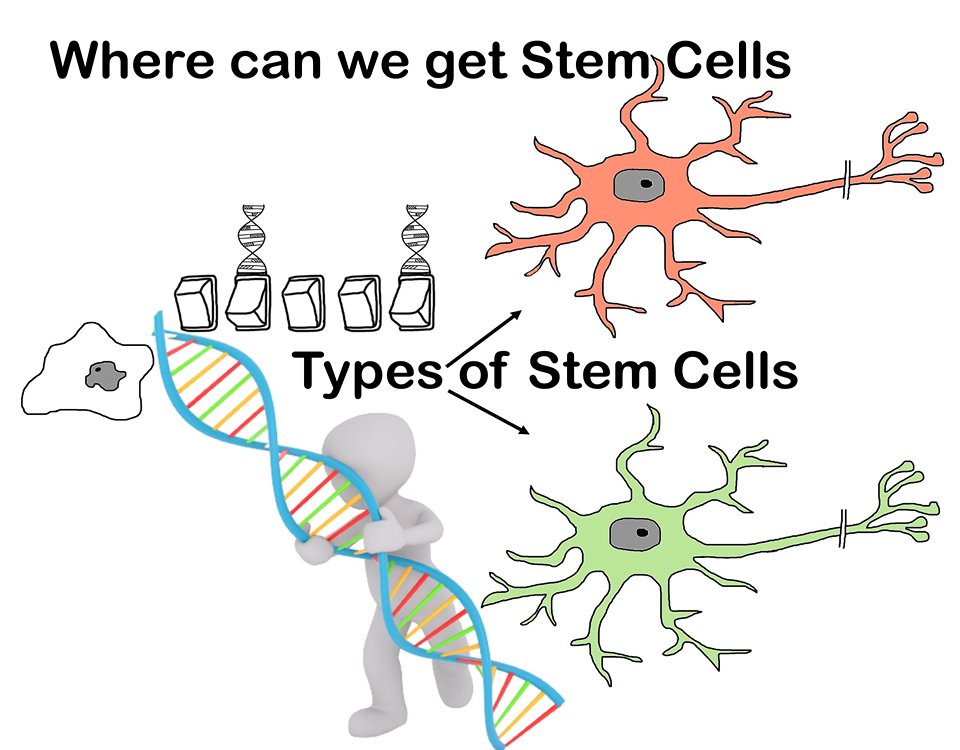
Where can we get Stem Cells
Stem cells have become a popular topic in recent years, with their potential for use in treating a wide range of medical conditions. But where can we get stem cells, and what are the options available? Where can we get Stem Cells – Types of Stem Cells
There are several sources of stem cells, each with its own unique properties and potential uses. Here are some of the most common sources of stem cells:
Embryonic stem cells: These stem cells are found in embryos that are just a few days old. They have the potential to differentiate into any type of cell in the body, which makes them extremely valuable for medical research. However, their use is controversial because obtaining them involves the destruction of embryos.
Adult stem cells: These stem cells are found in various tissues throughout the body, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and blood. They are less versatile than embryonic stem cells, but they can still differentiate into many different types of cells.
Umbilical cord stem cells: These stem cells are collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after a baby is born. They are similar to adult stem cells in that they are more limited in their differentiation potential than embryonic stem cells, but they can still be used in a variety of medical applications.
Induced pluripotent stem cells: These stem cells are created in a laboratory by reprogramming adult cells to behave like embryonic stem cells. They are a promising source of stem cells for medical research because they can be made from a patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of immune rejection. Where can we get Stem Cells – Types of Stem Cells
So where can you get stem cells? The answer depends on what type of stem cells you need and for what purpose. If you are interested in using stem cells for medical research, you may be able to obtain them from a research institution or a stem cell bank. If you need stem cells for medical treatment, your doctor may be able to obtain them from your own body (such as bone marrow) or from a donor (such as cord blood).
It’s important to note that while stem cells have enormous potential, their use is still largely experimental, and many treatments are not yet approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA. If you are considering using stem cells for medical purposes, it’s important to talk to your doctor and do your research to make an informed decision.
Where are stem cells found?
Embryonic stem cells: These stem cells are found in embryos that are just a few days old.
Fetal stem cells: These stem cells are found in the tissue of a developing fetus.
Adult stem cells: These stem cells are found in various tissues throughout the body, including bone marrow, adipose tissue (fat), brain, blood vessels, liver, skin, and muscle.
Umbilical cord stem cells: These stem cells are collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after a baby is born.
Amniotic fluid stem cells: These stem cells are found in the fluid that surrounds a developing fetus. Where can we get Stem Cells – Types of Stem Cells
Induced pluripotent stem cells: These stem cells are created in a laboratory by reprogramming adult cells to behave like embryonic stem cells.
Each type of stem cell has unique properties and potential uses, and researchers continue to explore their potential for treating a wide range of medical conditions. However, it’s important to note that the use of stem cells is still largely experimental, and many treatments are not yet approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA.
What is the best source of stem cells?
There is no definitive answer to the question of which source of stem cells is the best. Each type of stem cell has unique properties and potential uses, and the best source of stem cells depends on the specific medical condition being treated and the goals of the treatment.
Embryonic stem cells, for example, have the potential to differentiate into any type of cell in the body, which makes them extremely valuable for medical research. However, their use is controversial because obtaining them involves the destruction of embryos.
Adult stem cells, on the other hand, are found in various tissues throughout the body and are often used in medical procedures such as bone marrow transplants. They are less versatile than embryonic stem cells, but they can still differentiate into many different types of cells.
Umbilical cord stem cells are also a promising source of stem cells, as they are readily available and can be collected non-invasively after a baby is born. They are similar to adult stem cells in that they are more limited in their differentiation potential than embryonic stem cells, but they can still be used in a variety of medical applications.
Induced pluripotent stem cells have emerged as a promising source of stem cells for medical research and treatment. They are created in a laboratory by reprogramming adult cells to behave like embryonic stem cells, and they have the potential to be made from a patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of immune rejection.
The best source of stem cells depends on the specific medical condition being treated, the goals of the treatment, and the availability of the stem cells. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or a stem cell specialist to determine the most appropriate source of stem cells for a particular situation. Where can we get Stem Cells – Types of Stem Cells
Why are stem cells used?
Stem cells are used because of their unique ability to differentiate into different types of cells in the body. This ability makes them a promising tool for a wide range of medical applications, including:
Regenerative medicine: Stem cells can be used to regenerate damaged or diseased tissue in the body. For example, stem cells can be used to regrow skin in burn victims, to repair damaged heart tissue after a heart attack, or to restore function to damaged nerve tissue.
Disease modeling: Stem cells can be used to create models of human diseases, allowing researchers to study the disease in the laboratory and develop new treatments.
Drug development: Stem cells can be used to test the safety and efficacy of new drugs, reducing the need for animal testing and speeding up the drug development process.
Transplants: Stem cells can be used in bone marrow transplants to treat certain types of cancer and blood disorders, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
Gene therapy: Stem cells can be used to deliver genes to the body to treat genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia.
While stem cells hold great promise for a wide range of medical applications, their use is still largely experimental, and many treatments are not yet approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or a stem cell specialist to determine the most appropriate use of stem cells for a particular situation.
What are the advantages of using stem cells?
The use of stem cells offers several potential advantages in the field of medicine and research.
Regeneration: Stem cells have the unique ability to regenerate and repair damaged or diseased tissues in the body, which makes them valuable for treating a wide range of medical conditions.
Versatility: Stem cells can differentiate into many different types of cells in the body, which makes them a versatile tool for medical research and treatment.
Compatibility: Stem cells can be obtained from a patient’s own body, which reduces the risk of rejection and other complications associated with transplants.
Precision: Stem cells can be genetically modified to produce specific cell types, which allows researchers to create targeted therapies for a wide range of diseases.
Drug discovery: Stem cells can be used to screen potential drugs for safety and efficacy, which can accelerate the drug discovery process and reduce the need for animal testing.
Improved understanding of diseases: Stem cells can be used to create models of diseases, which allows researchers to study the underlying mechanisms of the disease and develop new treatments.
Reduced risk of side effects: Stem cells have the potential to replace or repair damaged tissues without the side effects associated with traditional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation.
While there are many potential advantages to the use of stem cells, it’s important to note that the use of stem cells is still largely experimental, and many treatments are not yet approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or a stem cell specialist to determine the most appropriate use of stem cells for a particular situation.
What diseases can stem cells cure?
It’s important to note that while stem cells hold great promise for the treatment of a wide range of diseases, their use is still largely experimental, and many treatments are not yet approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA. Additionally, the specific diseases that stem cells can cure or treat depend on the type of stem cells being used and the stage of research and development.
Here are some examples of diseases that are currently being studied for potential treatment with stem cells:
Blood disorders: Stem cells found in bone marrow or cord blood can be used to treat certain types of blood disorders, such as leukemia, sickle cell anemia, and lymphoma.
Neurodegenerative diseases: Stem cells have the potential to replace or repair damaged nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, which makes them valuable for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
Heart disease: Stem cells have been shown to improve heart function and reduce the risk of heart failure in patients with certain types of heart disease.
Diabetes: Stem cells have been used to produce insulin-producing cells in the laboratory, which could potentially be used to treat diabetes.
Autoimmune diseases: Stem cells have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve immune function in patients with autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Organ damage: Stem cells have been shown to repair or regenerate damaged tissue in the liver, kidney, and other organs.
While stem cells offer great potential for the treatment of many diseases, it’s important to note that many of these treatments are still in the early stages of research and development, and their efficacy and safety have yet to be fully established. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or a stem cell specialist to determine the most appropriate use of stem cells for a particular situation. Where can we get Stem Cells – Types of Stem Cells